Feeder-dependent mESC engineering (developed by Dr. Weimin Zhang)
(updated 4/12/2024)
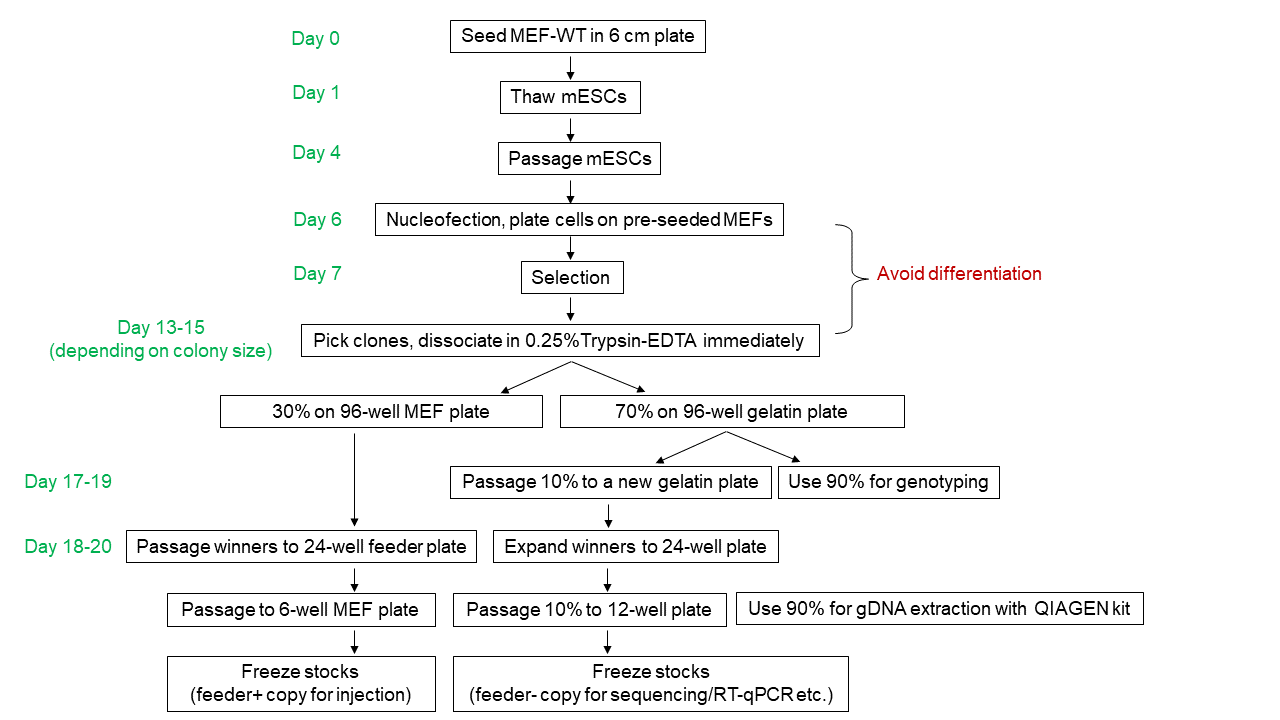
Graphic summary:
MEF medium (use for seeding feeder cells):
D-MEM (Life Technologies, 11965-118 ), 10% FBS (Gemini Bio-Products), 0.1 mM MEM Non-Essential Amino Acids (Fisher Scientific, 11140050), 1% Penicillin-Streptomycin-Glutamine (Invitrogen, 10378-016).
mES Medium (use for culturing mESCs on feeders):
KnockOut DMEM (Fisher Scientific, 10829018), 15% FBS (Hyclone, GE Healthcare Life Sciences, SH30070.03), 0.1 mM MEM NonEssential Amino Acids (Fisher Scientific, 11140050), 1% Penicillin-Streptomycin-Glutamine (Invitrogen, 10378-016), 1000U/mL LIF (EMD Milipore, ESG1107), 0.1mM 2-Mercaptoethanol (7 µl pure solution into 500 mL).
mESM+2i (use for culturing mESCs on gelatin):
Supplement CHIR (final 3µM) and MEKi (final 1µM) into mES Medium.
Protocol:
One day before thawing mESCs, seed (5x104 or 7.5x104 cells/cm2 according to vendor’s instructions) wild-type feeder cells (MEFs) into a gelatin (EMD Milipore, ES-006-B) coated 6 cm plate with MEF medium. (Note: after thawing the MEF, one more wash with MEF medium to thoroughly remove DMSO can be applied)
The next day, change MEF medium to mESM at least 2 hours before thawing.
Thaw ~1M of mESCs and seed on top of MEFs in mESM.
Change medium daily; passage mESCs at 1:3 ratio once the plate reaches 70-80% confluency (Note: always pre-seed MEFs one day before use).
Once the newly passaged mESCs reach 70-80% confluency, nucleofect (Mirus Bio, MIR 50118, Lonza nucleofector 2b, A-023 program) 2-3 million cells with your payload+Cas9-gRNAs. Plate nucleofected cells on a 10 cm MEF plate. (Note: Use MEFs expressing selection markers that match the payload. MEF depletion before nucleofection is unnecessary).
Change medium 12-16 hours after nucleofection to get rid of the nucleofection solution.
Add antibiotic selection with fresh medium 24-36 hours after nucleofection. Apply antibiotic selection for 1-2 days if doing transient Cas9-gRNA expression. Keep antibiotic selection the entire time for stable integrations.
Monitor plates daily until clones reach picking size.
Prepare a day in advance a gelatinized 96-well plate seeded with feeder cells.
On clone picking day:
Change 96-well MEF medium to 100 µl of mESM at least 2 hours before use.
Prepare a gelatinized 96-well plate at least 30 minutes before picking; aspirate gelatin and fill with 100 µl/well mESM.
Swap the mESM medium of the 10 cm plate to DPBS; adjust P20 pipet to 8 µl; pick colonies with 8 µl of DPBS and transfer to an empty round-bottom, non-treated 96-well plate. (Note: keep the 96-well lid on to avoid evaporation).
Once colony picking is finished, add 35 µl/well of pre-warmed 0.25% Trypsin-EDTA (Gibco, 25200056) to dissociate the colonies at 37°C for 7 min.
Add 100 µl/well mESM to neutralize the reaction immediately after 7 min.
Pipet 20 times to singularize the cells using a P200 multichannel pipet.
Transfer 100 µl of the cell suspension to the gelatin-coated 96-well plate prefilled with 100 µl mESM.
Transfer the rest (~40 µl) to the pre-seeded 96-well feeder plate.
Note: No need to change medium for the gelatin-coated plate for the first 2 days, then change medium with mESM+2i until genotyping PCR; change medium daily for the feeder plate.
Once the gelatin-coated plate becomes >50% confluent (usually takes 3-4 days depending on the size of initially picked colony), passage 10% of the cells to a new gelatin plate for proliferation; transfer 90% of cells to a PCR plate for crude gDNA extraction:
Spin down the PCR plate at 3,000 rpm for 3 min
Pipet out the supernatant.
Resuspend cell pellet with 30 µl lysis buffer: 0.3 mg/ml proteinase K (Thermo Scientific, EO0491) in TE.
Heat the cells on a thermal cycler at 50°C for 60 min followed by heat-inactivation at 98°C for 10 min.
Briefly spin-down the plate after boiling.
Use 1 µl of crude gDNA from previous step as template to screen for your desired edits using PCR-genotyping (in 10 µl GoTaq [Promega, M7123] PCR reactions): Include as many PCR assays as possible to exclude bad clones. Typically: left and right junctions, plasmid backbone, co-transfected plasmids (e.g. Cas9 or Cre expressing plasmids) etc. (Note: It’s recommended to complete the genotyping within a week after colony picking to avoid differentiation of mESCs on feeder plate).
Expand the correct clones from 96-well MEF plate to 24-well feeder plates.
Expand the correct clones from 24-well MEF plates to 6-well feeder plates. (Note: different clones may have different confluency, you might need to passage clones in several batches or adjust ratios to synchronize clones).
Record the morphology under a microscope. Images can be used later on to choose best clones to submit to blastocyst injection.
When feeder-dependent mESCs are 60-80% confluent, cryopreserve each well of the 6-well plate in 1-2 cryovials.
Passage feeder-free mESCs from the confluent 96-well gelatin plate to a 24-well plate. Once the 24-well plates become confluent, passage 10% of the cells to a 12-well plate. Pellet the remaining 90% cells for subsequent gDNA extraction with gDNA Mini kit (QIAGEN, 51306). Note: more efficient genotyping PCR can be performed using this high quality gDNA, including long amplicons that are hard to amplify from crude gDNA. Moreover, the additional passages help dilute residual DNA from transfected plasmids and from the feeders.
Submit column-purified gDNA samples for validation using capture-seq or similar methods.
Cryopreserve feeder--free mESCs when they reach ~70% confluency. Optional: freeze another pellet as backup and as a source for RNA extraction.
Visit Mouse embryonic stem (ES) cell culture for more information